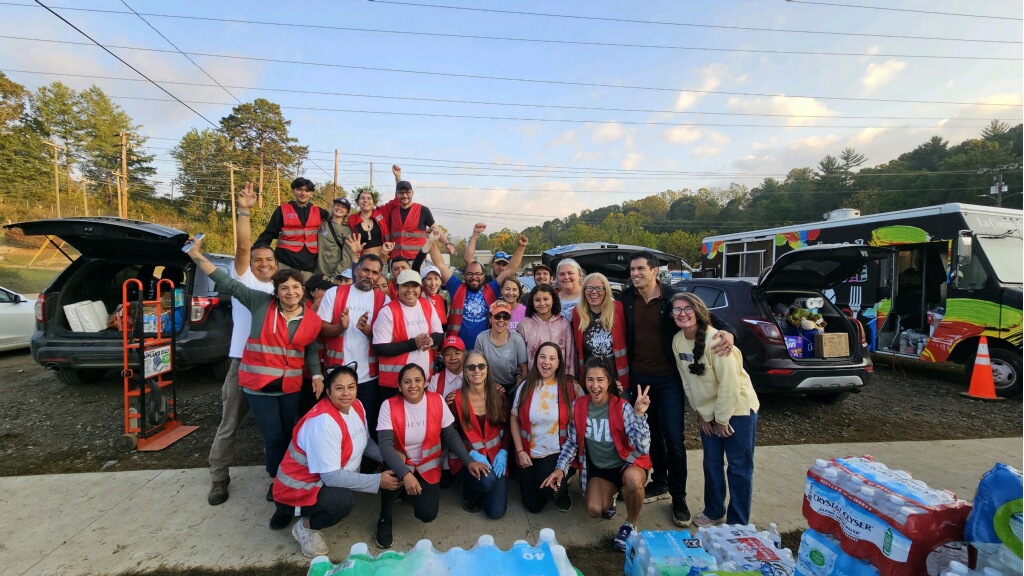
A powerful windstorm swept across Canada’s eastern coastline this week, leaving behind downed trees, damaged homes, and widespread power outages. While emergency services worked to respond, community volunteers emerged as a critical force, assisting neighbors, clearing debris, and supporting vulnerable populations. The event illustrates both the destructive power of extreme weather and the remarkable resilience and solidarity of Canadian communities in times of crisis.
The Storm and Its Immediate Impact
Meteorologists reported that the coastal windstorm brought sustained winds exceeding 120 kilometers per hour, accompanied by heavy rain and localized flooding. Key effects included:
-
Power Outages: Tens of thousands of households lost electricity as trees toppled onto power lines.
-
Transportation Disruptions: Roads were blocked by fallen trees and debris, delaying public transit and emergency vehicles.
-
Property Damage: Roofs, fences, and small structures were damaged, particularly in vulnerable coastal neighborhoods.
-
Marine Impacts: Strong winds and high tides disrupted ferry services and led to rough seas along the Atlantic coast.
Officials confirmed that no fatalities occurred, but several minor injuries were reported, largely due to slips, trips, and falling debris.